SOAP Notes Examples and Formating
Writing SOAP Notes: A Comprehensive Guide
As a healthcare professional, you are expected to create SOAP notes regularly. SOAP stands for:
Subjective
Objective
Assessment
Plan
These instructions will walk you through creating a SOAP note as well as provide examples and tips to help you craft professional SOAP notes with ease.
What is a SOAP Note and how is it defined?
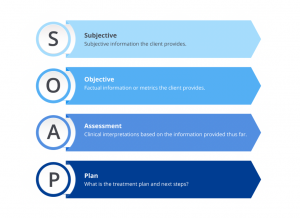
SOAP notes are structured methods of documenting patient data. Healthcare professionals utilize them to store, organize, and convey vital patient info. A SOAP note can be divided into the following components:
Subjective – This section contains information about the patient’s health status. This includes details such as symptoms and medical history.
Objective – This section includes information that can be measured and observed, such as vital signs, laboratory results, diagnostic imaging results, and physical exam findings.
Assessment – This section involves an assessment by a healthcare professional of both subjective and objective data. This includes both the diagnosis as well as any complications or comorbidities.
Plan – This section outlines the care plan for the patient created by a healthcare professional. It includes any prescriptions, referrals and any follow up appointments.
Soap Notes Image

Soap Notes Image

Soap Notes Image
Writing SOAP notes: Tips
Writing SOAP notes should be kept concise and precise. Steer clear of technical terms or jargon that could be confusing; use plain, straightforward language whenever possible.
Use Objective Language. When crafting the objective section of a note, it’s essential to use neutral language that relies on observed facts rather than opinions or assumptions.
Utilize the Correct Medical Terminology: Using Medical terminology in healthcare settings, frequently helps other healthcare professionals comprehend what you’re saying and provide the best care for the patient.
Be specific and precise: Give detailed information about the patient’s medical history and condition so other healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding their care.
Avoid Abbreviations
Stick with the SOAP Note Format: Be sure to follow the SOAP format and include all four parts of your note. Doing this will guarantee that you organized your document clearly which in turn makes it easy to understood.
Writing the Subjective Section
The subjective section of a SOAP note includes information provided by the patient about their health status. Here are some tips for crafting this section effectively.
When possible, include quotes: If the patient provides a quote about their condition, include it in your note to give an accurate representation of their experience. This will give readers a more complete overview of what the patient has gone through.
Include the chief complaint of the patient: in the subjective section.
Include the patient’s medical history: This provides context for their current condition. In the subjective section, make sure to include any pertinent medical history.
Include information about the patient’s past social life: This can provide context for current conditions. Also include details about their occupation and lifestyle.
Example:
S: Patients report feeling tired and run down over the past two weeks. They experience occasional headaches as well as difficulty sleeping.
Writing the Objective Section
The SOAP note’s objective section should contain information that one can measure and observe. Here are some tips for crafting this section effectively.
Begin with vital signs: Pay close attention to signs such as blood pressure, pulse rate and respiratory rate. These measures are important indicators of a patient’s overall wellbeing.
Include Any Findings From a Physical Exam: Any physical exam findings that are pertinent to the patient’s health should be included. These could include skin color, texture, heart sounds and abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system.
Include Laboratory Results: Any laboratory work related to the patient’s health condition should be included. This could include blood tests, urine tests or any other relevant lab work.
Include diagnostic imaging results: These may include X-rays, CT scans and MRIs. These images provide vital insight into a patient’s health condition.
Example:
O: Blood pressure 120/80 mmHg, pulse rate 80 beats per minute, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute and temperature 98.6degF were all normal on physical exam; laboratory work revealed normal CBC and metabolic panels while chest X-ray revealed no signs of pneumonia.
How to Craft the Assessment Section
In a SOAP note’s assessment section, healthcare professionals analyze both subjective and objective data. Here are some tips for crafting this section effectively.
Include a diagnosis: You make diagnoses based on objective and subjective data to provide an overview of the patient’s current health condition. This allows for more accurate monitoring and management of their medication needs.
Include any complications or comorbidities in the assessment section to ensure other healthcare professionals are aware of any health issues.
Proper Medical Terminology Is Used: To accurately convey a patient’s situation, utilize terminology common within the healthcare industry.
Example:
A: The patient has been diagnosed with insomnia without any associated conditions or complications.
How to Write the Plan Section of a SOAP Note
The plan section in an SOAP note outlines the patient’s plan of care as provided by their healthcare professional. Here are some tips on crafting this section effectively.
Prescriptions: Make a note of any medication that you have prescribed, including its side effects and dosage information.
Referrals: Include this information in your plan section if the patient requires referral to a specialist for further care.
Include Information About Follow-Up Appointments: Make sure the patient knows about any necessary follow-up appointments.
Example:
P: For two weeks, prescribe 5mg of melatonin at bedtime. Refer patient to a sleep specialist for further assessment and set up an appointment within three weeks to follow-up.
Conclusion
SOAP notes are an integral part of patient care. To ensure you have written the notes professionally and effectively, follow these examples and tips provided here. To make the note simple to comprehend and organized, utilize medical terminology whenever possible.


